
Electrification
Electrification
Compared with traditional cars, the main difference between electric vehicles and traditional fuel vehicles lies in key components such as drive motors, speed controllers, power batteries, and on-board chargers. Car mounted batteries are mainly used as energy sources, while motors serve as power sources to drive vehicles. Due to the complex working environment of automobiles, electric vehicles require a higher level of electronicization, therefore automotive PCBs have extremely high reliability requirements.
Electric vehicles typically require various printed circuit boards (PCBs) to control different systems and functions, including:
Motor control: used to manage motors to provide smooth and quiet acceleration, torque, and efficiency.
Battery management: used to manage the vehicle’s battery system, including monitoring battery charging and discharging to ensure safe and efficient operation of the battery.
Power electronic devices: used to convert the energy stored in batteries into the electrical energy required to drive electric motors.
Charging control: used to manage the charging of batteries, including controlling the charging rate, monitoring the charging process, and ensuring the safety of the charging process.
Energy management: used to manage the energy flow between batteries, electric motors, and other systems (such as climate control and entertainment systems).
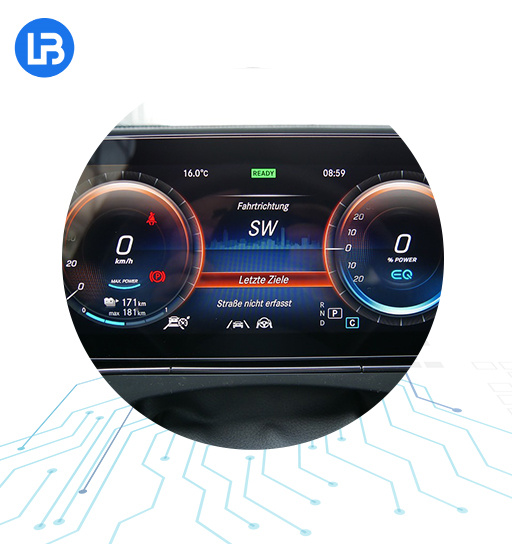
Information and entertainment system: an information and entertainment system used to manage vehicles, including audio systems, navigation systems, and in car entertainment systems.
Remote Information Processing: A remote information processing system for vehicles, including communication systems such as GPS, Bluetooth, and Wi Fi.

Electrification01

Electrification02

Electrification03
Contact Us
Chengdu LUBANG Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.
-

Phone
-
E-mail
-

Whatsapp
WhatsApp
-
Top











